In today’s data-driven world, we generate an enormous amount of information daily. Storing and managing this data efficiently is critical, especially when duplicate files or data take up unnecessary space. This is where deduplication comes in—a method to remove redundant copies and optimize storage.
Let’s dive into deduplication in simple terms.
Table of Contents
What Is Deduplication?
Deduplication is the process of eliminating duplicate data from a dataset. Imagine you save the same photo on your computer multiple times under different filenames. Each of those copies takes up space, but deduplication ensures only one copy is stored, saving space and improving efficiency.
How Does Deduplication Work?
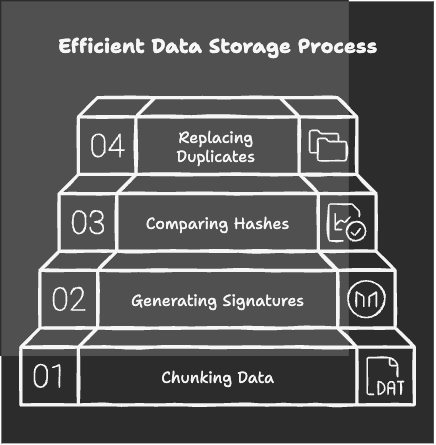
Deduplication uses a process to identify and remove duplicates. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Chunking Data
Large files are broken into smaller chunks of fixed or variable size. - Generating Unique Signatures
Each chunk is analyzed, and a unique identifier called a “hash” is created using algorithms like MD5, SHA-1, or SHA-256. Think of this as assigning a fingerprint to each chunk. - Comparing Hashes
The system checks whether the hash already exists in the storage. If it does, the chunk is not stored again. If it doesn’t, it’s added to the storage. - Replacing Duplicates
Duplicate chunks are replaced with pointers to the original data. This way, only one copy exists, while the duplicates are virtually linked to the original.
Types of Deduplication
- File-Level Deduplication
Compares entire files and eliminates duplicates. For example, if two files are identical, only one is kept. - Block-Level Deduplication
Breaks files into smaller chunks and compares each block. This method is more efficient, as even if files are slightly different, identical blocks can still be deduplicated. - Inline vs. Post-Process Deduplication
- Inline: Deduplication occurs in real-time as data is written to storage.
- Post-Process: Deduplication happens after the data is stored.
Benefits of Deduplication
- Saves Storage Space
By removing duplicates, you can store more data in less space. - Improves Backup Efficiency
Redundant data is removed, so backups are faster and require less storage. - Cost Savings
Less storage means lower costs for hardware and maintenance. - Streamlines Data Management
Managing a smaller, deduplicated dataset is easier and less error-prone.
Real-Life Examples of Deduplication
- Cloud Storage Services
Services like Google Drive and Dropbox use deduplication to save space and provide faster uploads. - Backup Software
Tools like Veeam, Acronis, and others optimize storage by deduplicating backup files. - Email Servers
Deduplication ensures only one copy of an attachment is stored, even if sent to multiple recipients.
[Video] Understanding Deduplication: A Beginner’s Guide
Conclusion
Deduplication is a simple yet powerful concept that ensures storage is used efficiently by removing unnecessary duplicates. Whether you’re managing personal files or handling enterprise data, understanding and applying deduplication can save space, time, and money.